"Run as Administrator": What Does It Mean?
Every bit a TechSpot reader you've surely opened software as an admin on Windows before -- maybe equally recently as today -- then the function probably isn't foreign to you. Even so, we were curious to know more than about what happens under the hood of Windows when you tell the operating system to run a plan as an administrator, and why this procedure is necessary in the first place.
Those of you who made the transition from Windows XP to Vista will probably remember the introduction of "User Access Control" (UAC) or "Mandatory Integrity Command" (MIC). The security characteristic prompts you when software tries making changes to your system and rests at crux of why applications sometimes require "elevated" access. UAC remains a fundamental component of Windows x'due south security to mitigate the affect of malware, although the overall experience has been relaxed and improved in subsequent releases.
When you log in to Windows, your account is assigned a token that contains identifying information including your user groups and privileges such as read, write, and execute permissions.
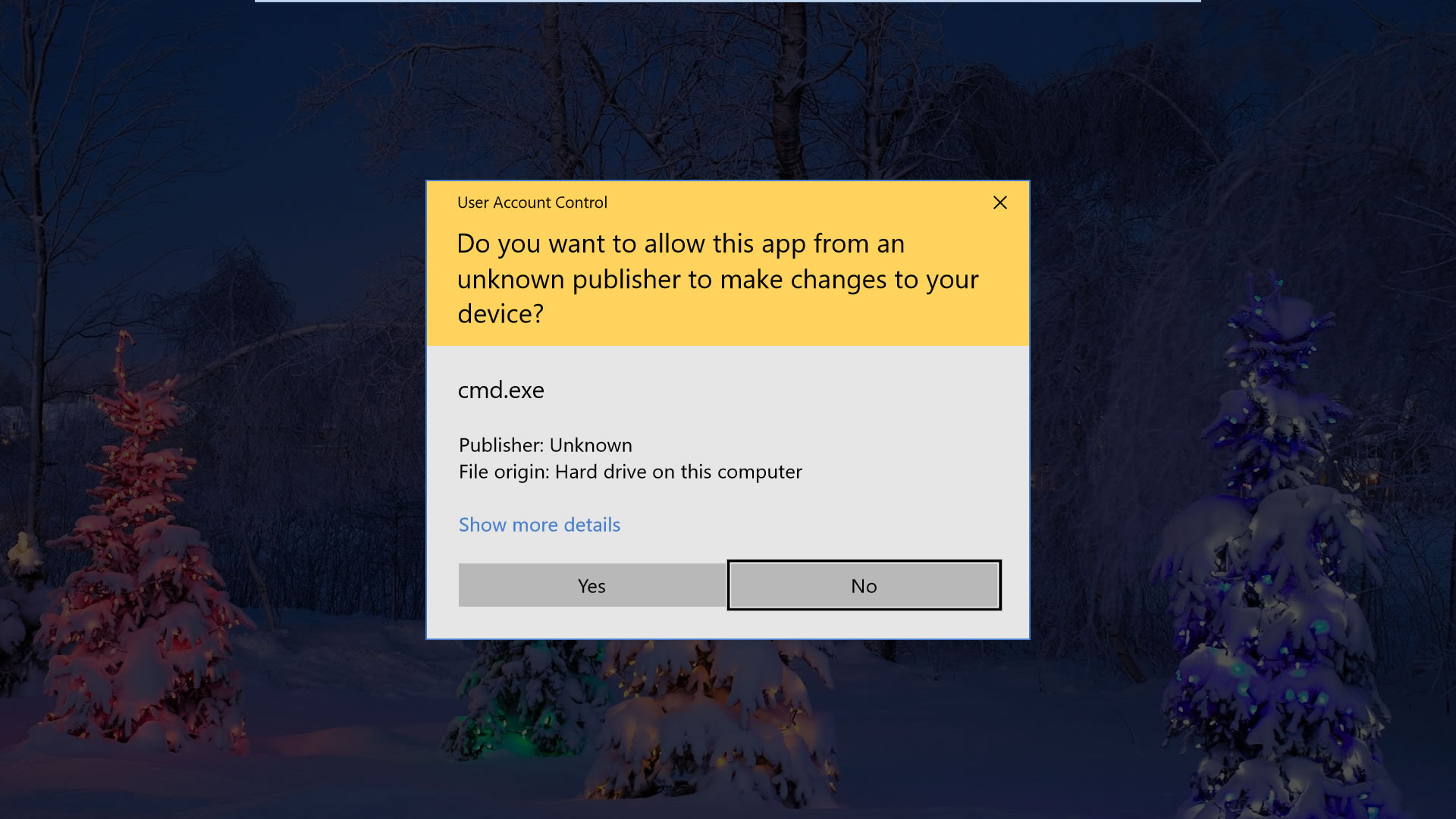
Among the information in that token is an integrity level which is used by the operating arrangement determine the trustworthiness of objects like files, registry keys for the purpose of informing users when installations are existence launched also as isolating processes from having unnecessary admission to system files.
Editor'south Note: This feature was originally published on October 2022. It'due south just as relevant today, so we've bumped it as part of our #ThrowbackThursday initiative.
The Windows Mandatory Integrity Control (MIC) mechanism has at least half-dozen different integrity levels: untrusted, low, medium, high, arrangement and trusted installer. By default, a standard user account has a medium integrity, which is the maximum level available for a process to be created when you lot open an executable file without providing elevated access via admin credentials.
When y'all right-click on a file or program and cull "Run equally administrator," that process (and only that process) is started with an administrator token, thus providing high integrity clearance for features that may crave the additional access to your Windows files etc.
The different Windows integrity levels:
- Untrusted Integrity: Given to anonymous processes.
- Depression Integrity: Commonly used for Web-facing software such as browsers.
- Medium Integrity: Practical to standard users and used for almost objects.
- High Integrity: Ambassador-level access, generally requires tiptop.
- System Integrity: Reserved for the Windows kernel and core services.
- Trusted Installer: Used for Windows Updates and system components.
Processes started past opening an exe from a Windows account with medium clearance will have that integrity level unless the executable file is set to low, and developers are encouraged to use the everyman access possible, ideally avoiding instances where software will require high integrity to thwart unauthorized lawmaking (malware) from taking root.
The practise of "least-privilege" pattern is applied to Windows' own administrator accounts, which receive both standard and admin-level tokens upon logging in, using standard/medium integrity access when possible instead of loftier.
Although Microsoft recommends confronting running programs as an administrator and giving them loftier integrity admission without a skillful reason, new information must be written to Programme Files for an awarding to be installed which will e'er require admin access with UAC enabled, while software such as AutoHotkey scripts will oftentimes need elevated condition to function properly.
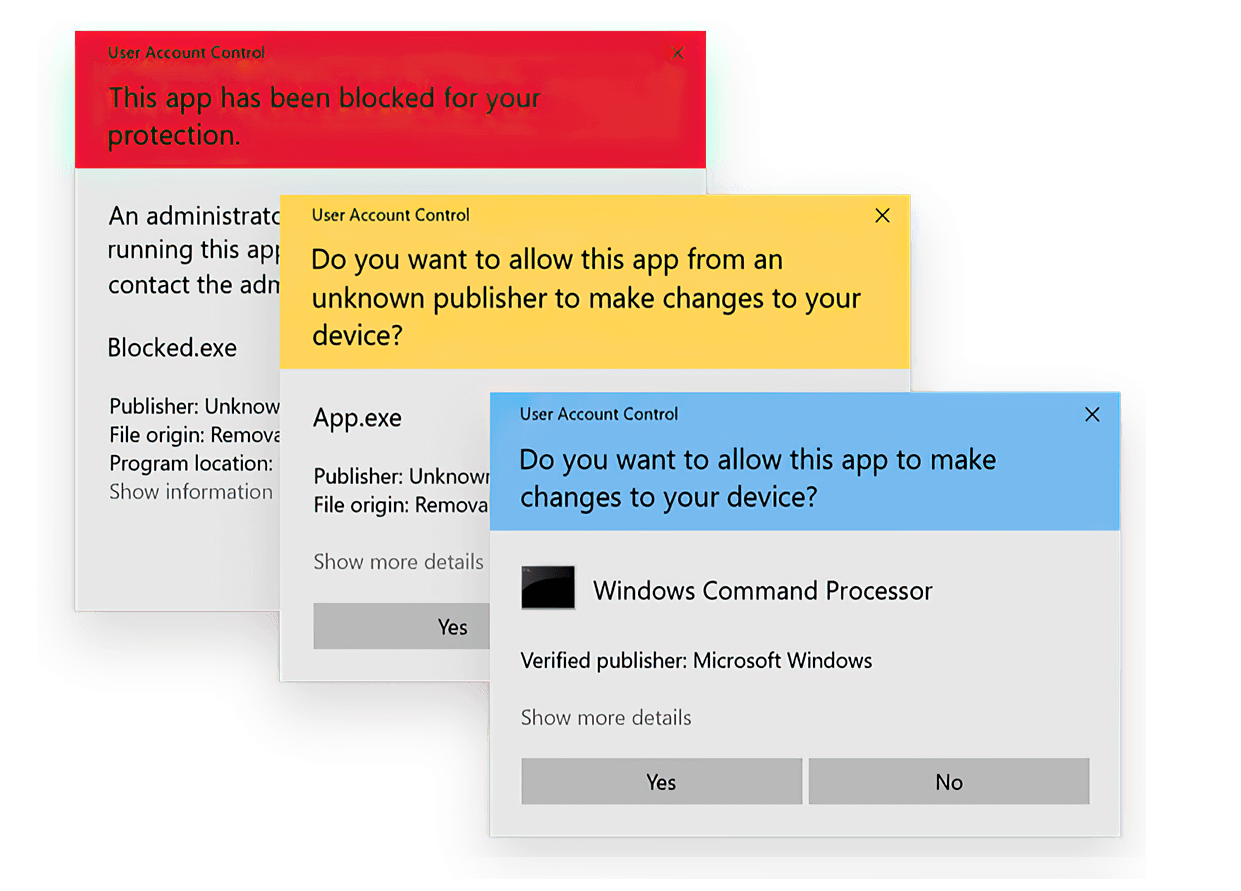
Here are all the ways we could find to open up executable files with administrator admission (high integrity) on Windows 10, including some methods that will configure software to always open up with elevated access:
Ways to run a programme as an administrator on Windows
Starting with the most obvious: you tin can launch a program as an administrator by right-clicking on the executable file and choosing "Run as administrator."
As a shortcut, holding Shift + Ctrl while double-clicking the file volition too start the plan as an admin.
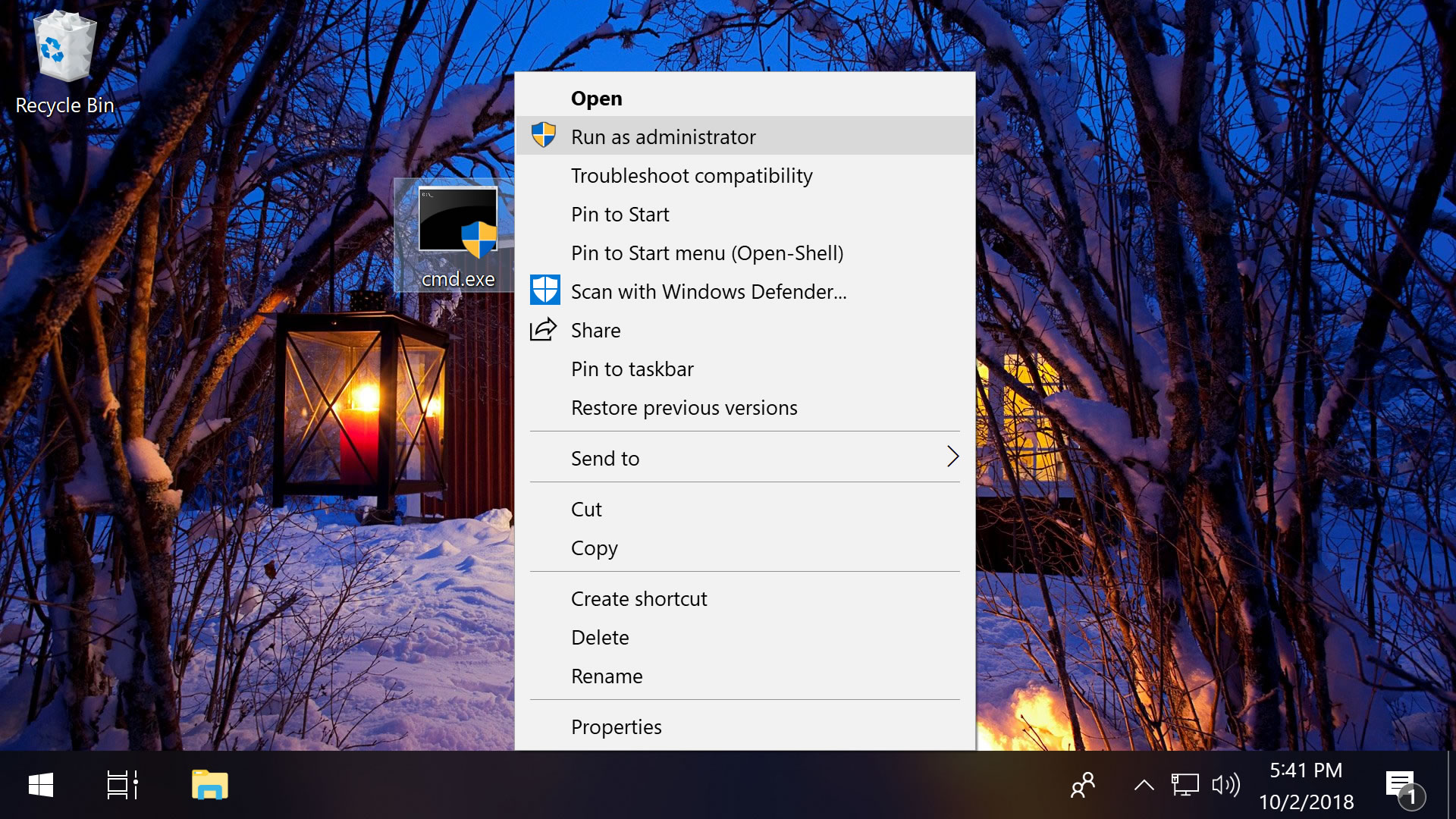
Separately, holding merely Shift while you right-click on the file will add together "Run every bit a dissimilar user..." to the context carte du jour, which opens a screen where you lot can enter another user's credentials, including the administrator account (the username is Administrator and may not have a password if you haven't applied one).
These locations also have shortcuts to admin admission...
Beginning Menu : Right-click an executable like anywhere else for the choice to launch a program equally an administrator.
Taskbar: Click a programme on your taskbar to open the jump list, then correct-click the exe from that carte for the admin option.
File Explorer: Select the file in File Explorer > Click Manage in the Ribbon menu upwards height > Choose "Run as administrator."
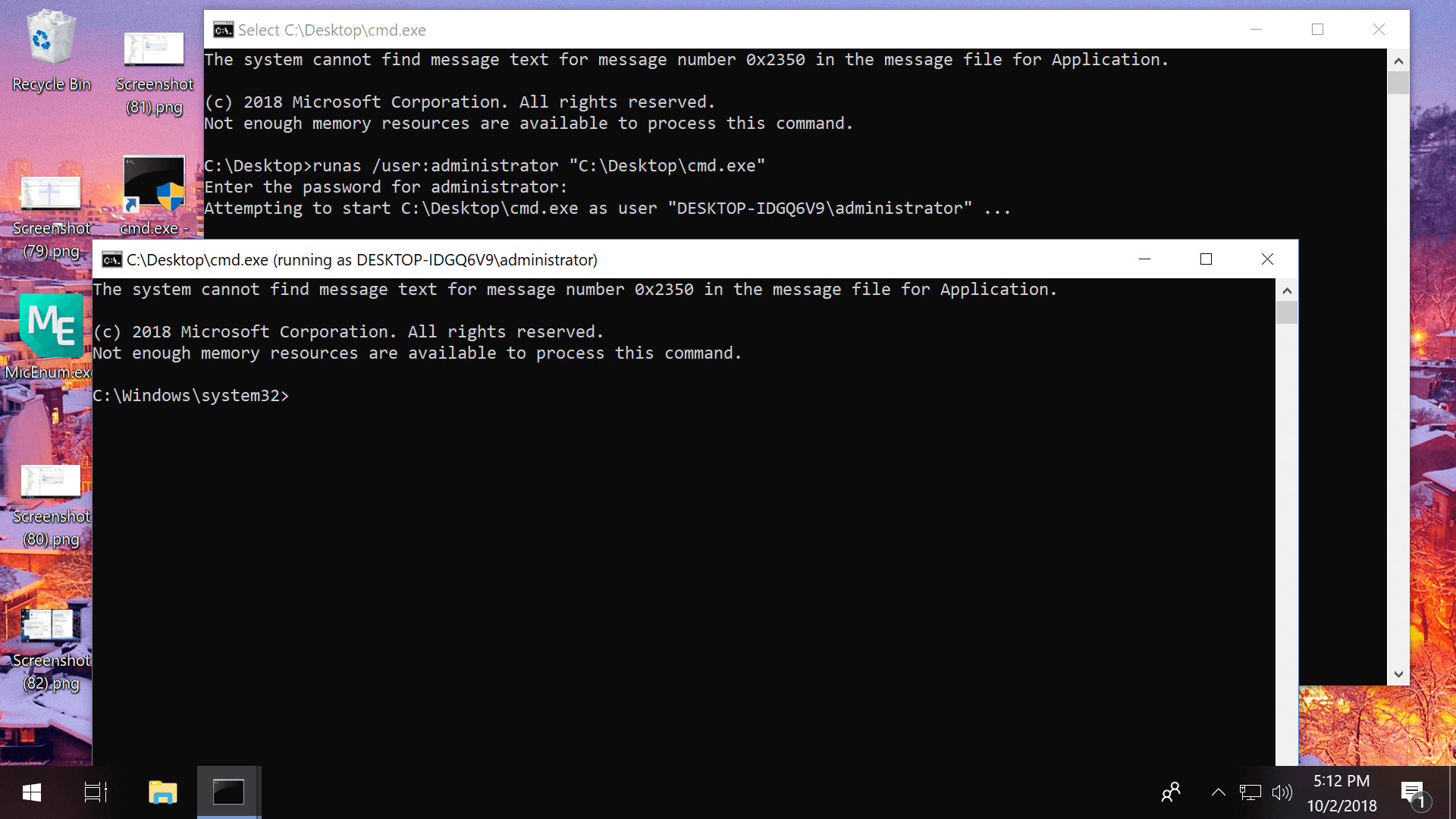
Run prompt: Enter this line into Run (Windows key + R): RunAs.exe /user:Administrator "cmd.exe"
Command Prompt: From the command line, enter this with your file location: runas /user:ambassador "C:\Users\TechSpot\Desktop\file.exe"
Task Director: Click File > Run new task > Check the box side by side to "Create this task with administrative privileges" > Enter the location of your file (case: C:\Users\TechSpot\Desktop\file.exe )
Task Scheduler: When creating a new task (Action > Create Job), enable these settings in the "Full general" tab: "Run whether user is logged on or non" and "Run with highest privileges"
Note that the Control Prompt method didn't work until we enabled the Administrator account and inverse another setting that would allow the command to exist entered without a password:
- Search Start or Run for compmgmt.msc > Go to Local Users and Groups > Users > double-click on Administrator and uncheck "Account is disabled"
- Search Start or Run for gpedit.msc > Go to Calculator Configuration > Windows Settings > Local Policies > Security Options > Double-click the pick Accounts: Limit local business relationship utilize of blank passwords to console logon online and choose Disable
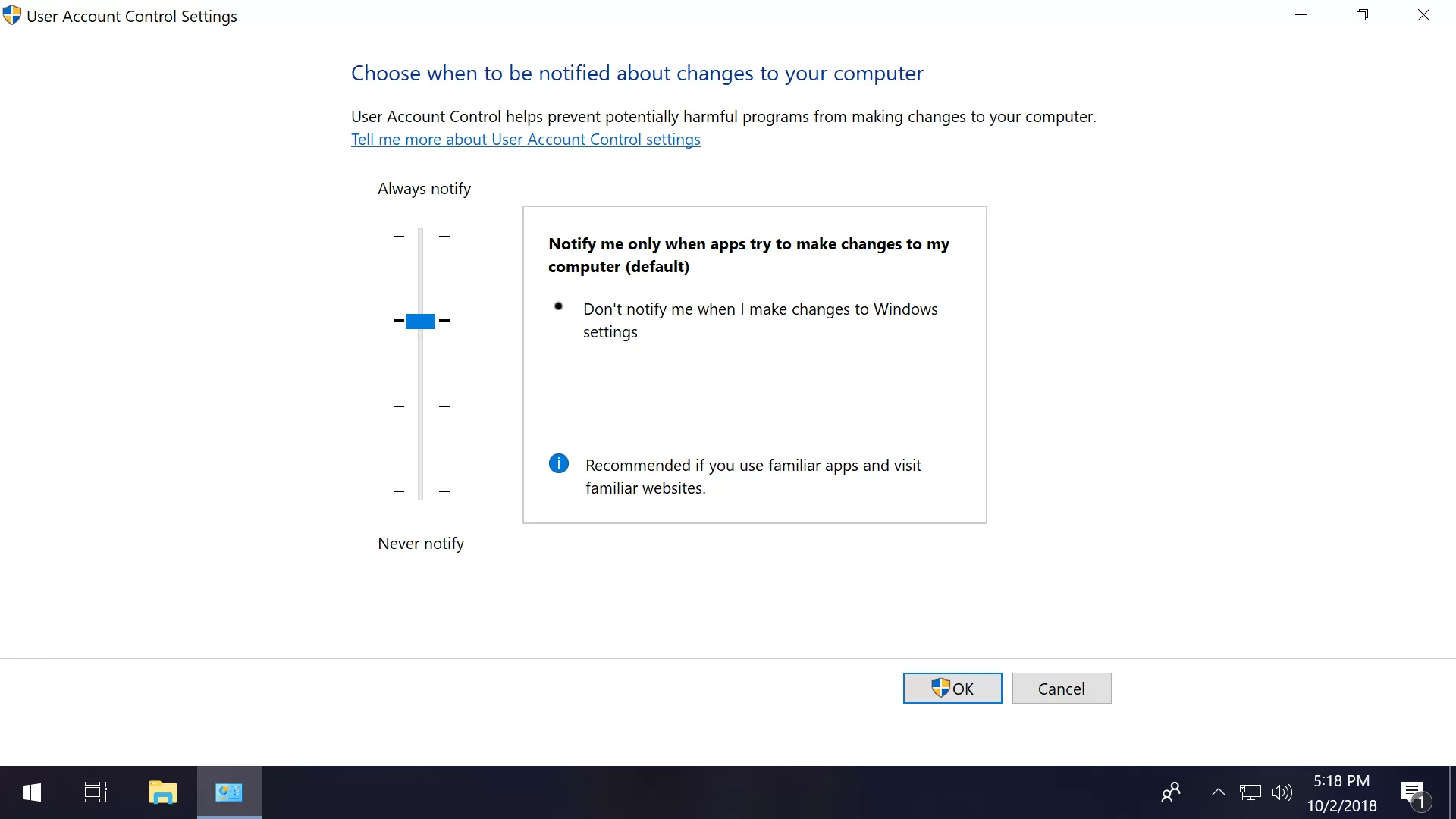
Also, in the same section of the Grouping Policy Editor (gpedit.msc) that we only mentioned are a range of options to fine-tune Windows' User Account Control settings (scroll all the way downwardly).
How to set programs so they ever outset as an admin
Given Microsoft'due south philosophy of providing programs with the least amount of admission possible, configuring an application to always run equally an ambassador is generally not recommended but sometimes convenient when the software always requires top so yous don't take to jump through those hoops every fourth dimension.
Here are a few ways to accomplish that:
Always run as admin from a shortcut: Right-click on a shortcut file > Shortcut tab > Advanced > Check the box to "Run as administrator"
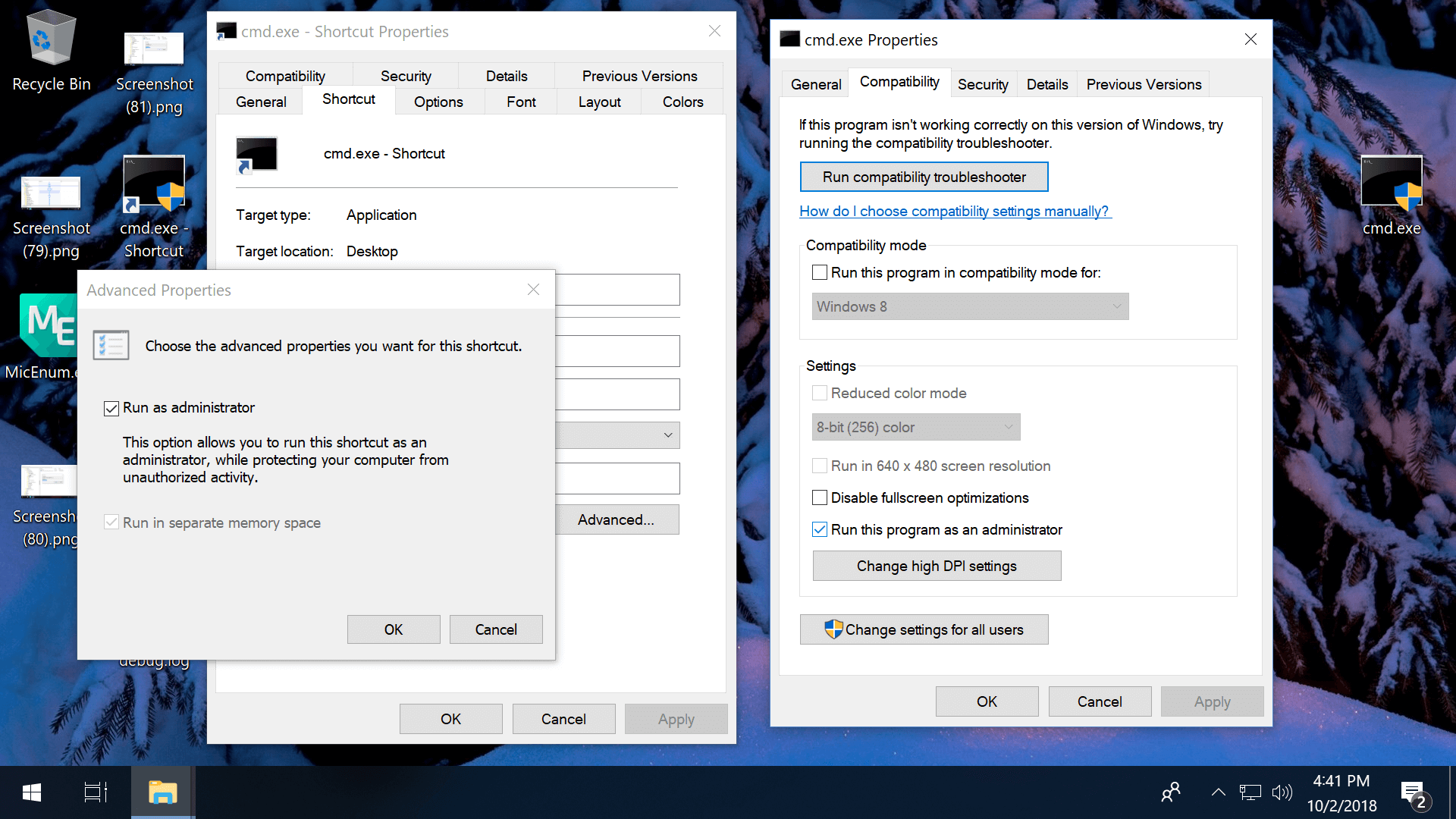
Annotation that you can create a shortcut file past right-clicking the primary exe, and that if you copy the shortcut into C:\Users\TechSpot\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup the program will automatically beginning with Windows as you sign in.
Always run every bit admin via Compatibility Backdrop: Right-click on an exe > Properties > Compatibility tab > Cheque the box to "Run this program as an ambassador."
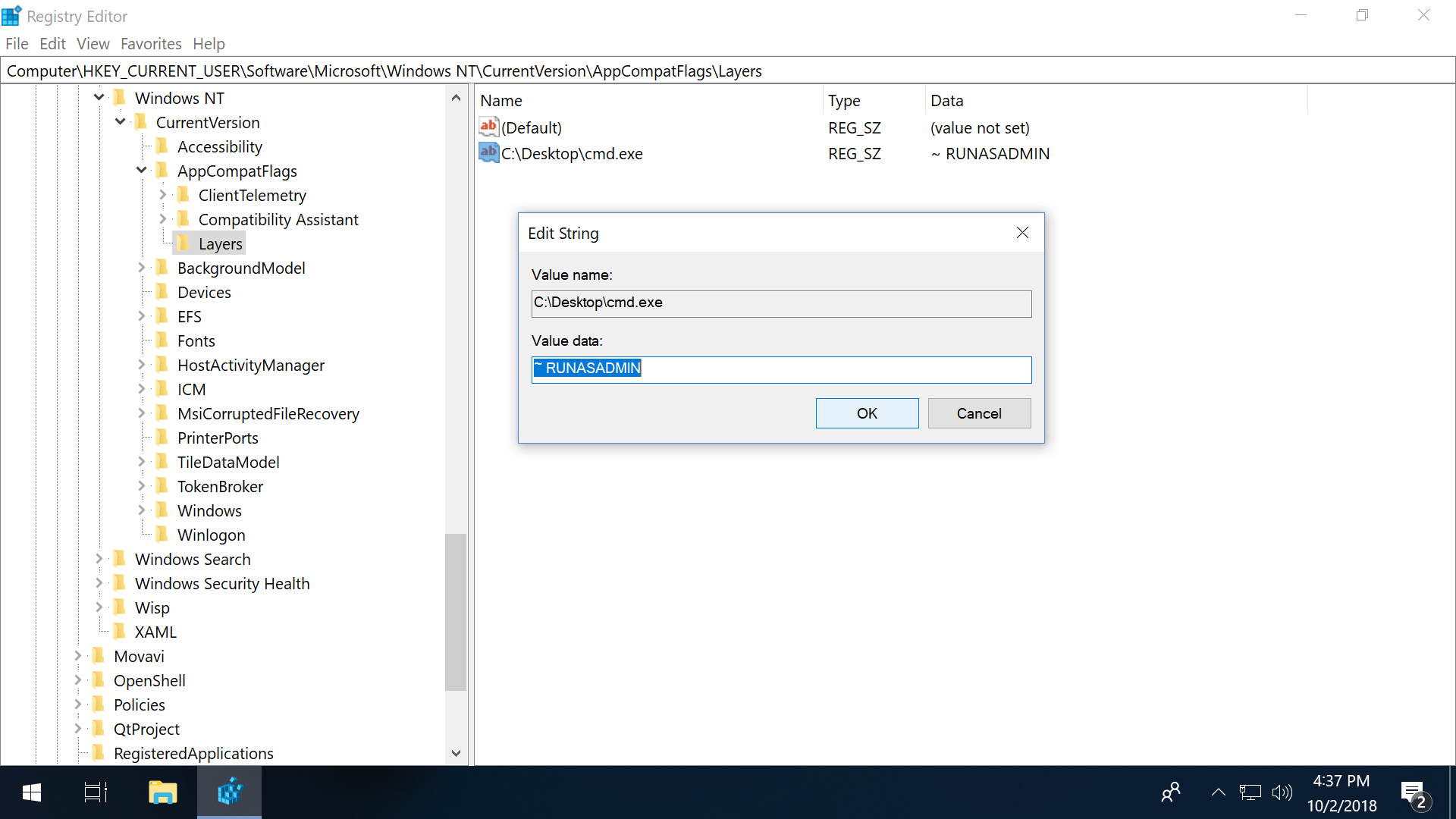
E'er run every bit admin via the Registry Editor:
- Navigate to: HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\AppCompatFlags\Layers
- If "Layers" is missing, correct-click AppCompatFlags and add a new fundamental named Layers
- Right-click Layers (either the folder or in the right pane) an create a new String Value
- Set the value name equally the full path of the exe file
- Set up value information as ~ RUNASADMIN
Bonus Tips
#1
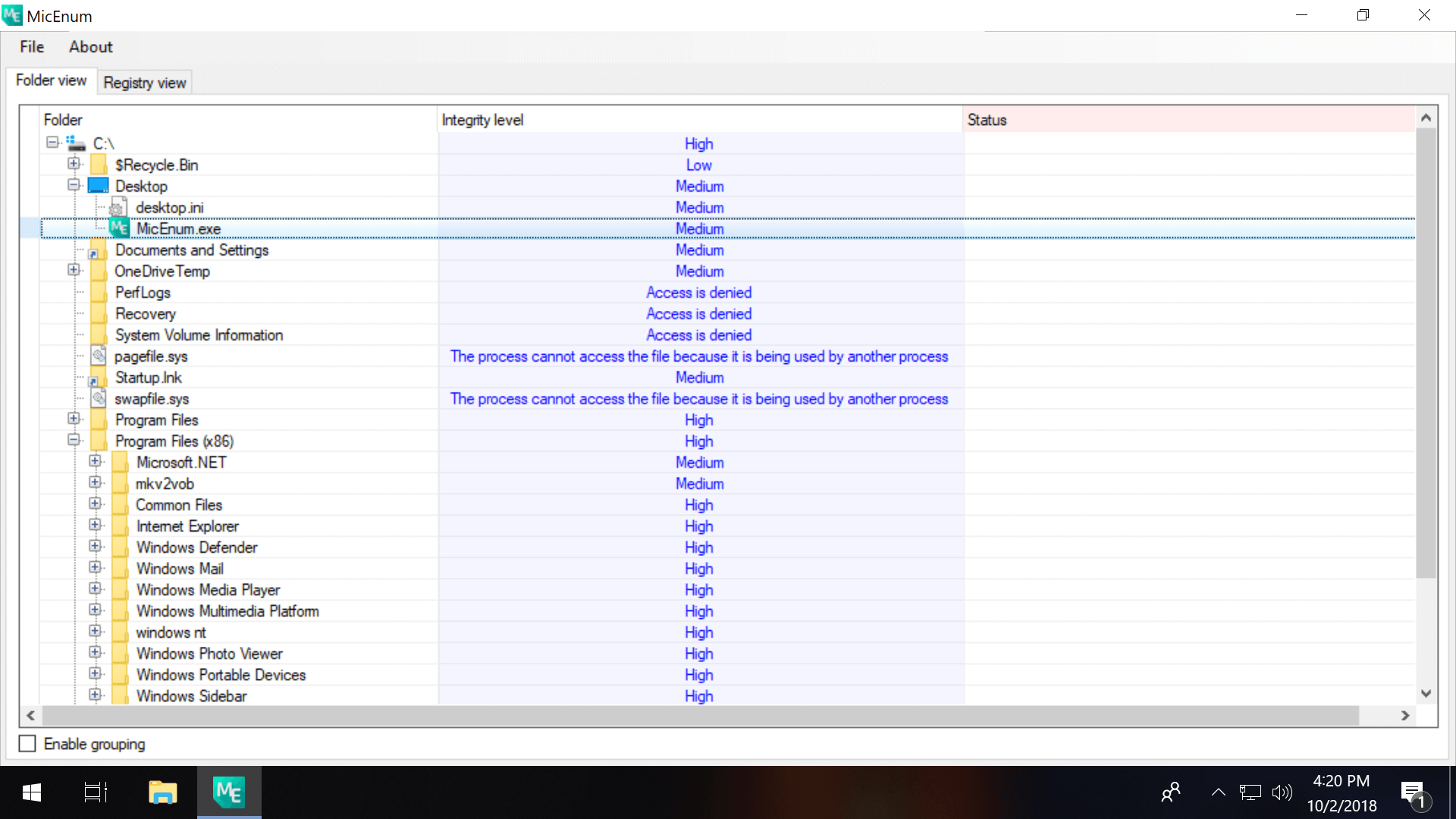
3rd-party software like MicEnum tin generate a listing of Windows files/folders and their integrity levels, including the ability to set a new integrity level as well equally browse in both folder and registry views.
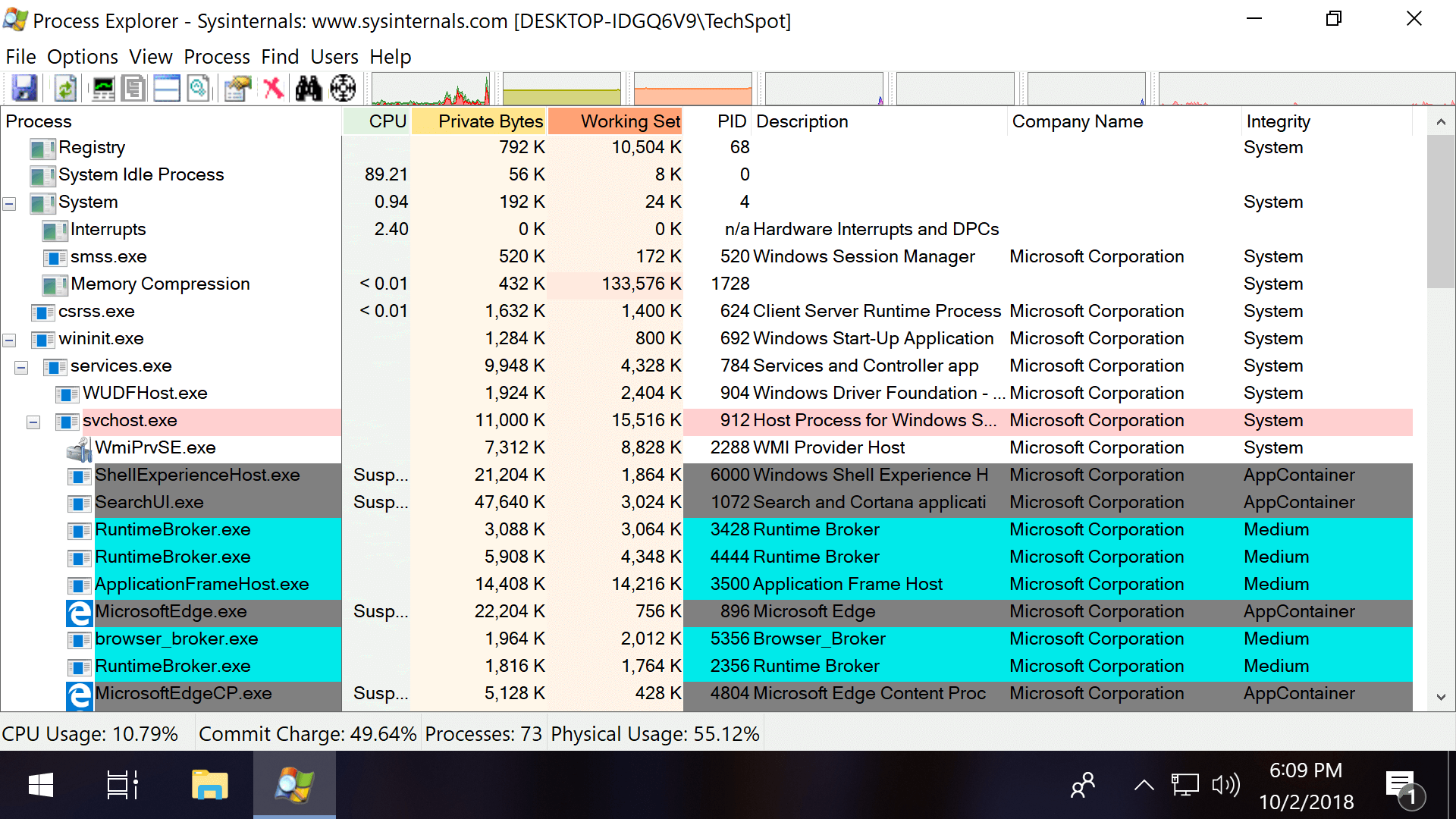
Process Explorer (pictured in the intro of this article) also has the ability to display integrity levels if you correct click the horizontal bar with CPU, Private Bytes etc. and open the properties. Then check the box next to Integrity Levels.
#2
On a new Windows installation, the starting time user account created is a local ambassador account while subsequent accounts are standard users. By default, the congenital-in administrator account is disabled.
You tin enable the business relationship and then it'southward available when y'all log in to Windows past entering this line into Command Prompt (use "no" to disable it again): net user administrator /active:yes
#3
Microsoft has different utilities such as Height PowerToys and PsExec which tin besides exist used to gain administrator access but bridge across the telescopic of this guide.
More Useful Tips
- How to Optimize Your Internet Connexion for Gaming
- How to Customize the Windows x Context Menu
- A Compilation of Command Prompt Tips, Tricks & Cool Things Yous Tin can Do
- Essential Apps You Should Install on a New PC Running Windows or macOS
Source: https://www.techspot.com/guides/1718-run-as-administrator-explained/
Posted by: reillyaceir1939.blogspot.com


0 Response to ""Run as Administrator": What Does It Mean?"
Post a Comment